
This SAMs assisted area-selective ALD method of core shell structure fabrication greatly expands the applicability of ALD in fabricating novel structures and can be readily applied to the growth of NPs with other compositions. Such core shell structures can be realized by using regular ALD recipes without special adjustment. Microwave power, the flow rate of Ar and O2 gas were set to 2 kW, 10 and 8 L/min, respectively, as stable plasma processing conditions. This work describes the use of laser ablation in liquid to fabricate graphene oxideZrO2/p-Si heterojunction photodetectors. High-performance photovoltaic devices with coreshell structures can be obtained by optimizing the preparation conditions. The size, shell thickness and composition of the NPs can be controlled precisely by varying the ALD cycles. The core nanoparticle deposition process was evaluated by measuring the thickness of the grown thin film. The superior structural, optical, and electrical characteristics of the coreshell structure make it a potential issue in optoelectronic devices.
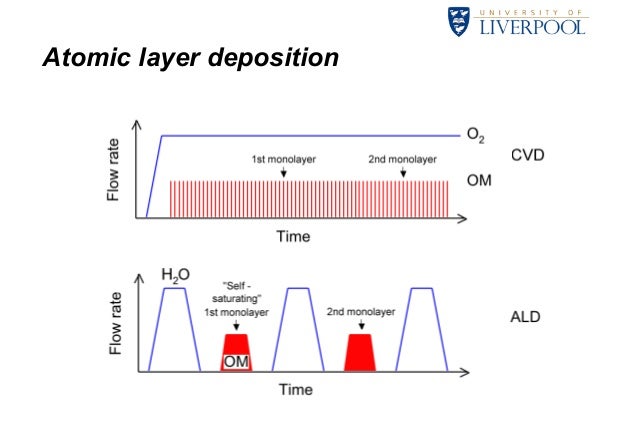
Since new nucleation sites can be effectively blocked by surface ODTS SAMs in the second deposition stage, we demonstrate the successful growth of Pd/Pt and Pt/Pd NPs with uniform core shell structures and narrow size distribution. Take the usage of pinholes on SAMs as active sites for the initial core nucleation, and subsequent selective deposition of the second metal as the shell layer.

The method involves utilizing octadecyltrichlorosilane (ODTS) self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) to modify the surface. We report an atomic scale controllable synthesis of Pd/Pt core shell nanoparticles (NPs) via area-selective atomic layer deposition (ALD) on a modified surface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
